The gen dao command is the most frequently used command in the CLI and is crucial for the accurate implementation of the framework’s engineering specifications. This command is used to generate dao data access objects, do data transformation models, and entity instance data model Go code files. Due to the numerous parameters and options for this command, it is recommended to manage generation rules using configuration files.
For an introduction to the framework's project engineering specifications, please see the section Code Layering.
Usage
In most scenarios, execute gf gen dao in the project's root directory. Below is the command line help information. The following command line output is for reference only:
$ gf gen dao -h
USAGE
gf gen dao [OPTION]
OPTION
-p, --path directory path for generated files (default: "internal")
-l, --link database configuration, the same as the ORM configuration of GoFrame
-t, --tables generate models only for given tables, multiple table names separated with ','
-x, --tablesEx generate models excluding given tables, multiple table names separated with ','
-sp, --shardingPattern sharding pattern for table name, e.g. "users_?" will be replace tables "users_001,
users_002,..." to "users" dao
-g, --group specifying the configuration group name of database for generated ORM instance,
it's not necessary and the default value is "default" (default: "default")
-f, --prefix add prefix for all table of specified link/database tables
-r, --removePrefix remove specified prefix of the table, multiple prefix separated with ','
-rf, --removeFieldPrefix remove specified prefix of the field, multiple prefix separated with ','
-j, --jsonCase generated json tag case for model struct, cases are as follows:
| Case | Example |
|---------------- |--------------------|
| Camel | AnyKindOfString |
| CamelLower | anyKindOfString |
| Snake | any_kind_of_string |
| SnakeScreaming | ANY_KIND_OF_STRING |
| SnakeFirstUpper | rgb_code_md5 |
| Kebab | any-kind-of-string |
| KebabScreaming | ANY-KIND-OF-STRING | (default: "CamelLower")
-i, --importPrefix custom import prefix for generated go files
-d, --daoPath directory path for storing generated dao files under path (default: "dao")
-tp, --tablePath directory path for storing generated table files under path (default: "table")
-o, --doPath directory path for storing generated do files under path (default: "model/do")
-e, --entityPath directory path for storing generated entity files under path (default: "model/entity")
-t0, --tplDaoTablePath template file path for dao table file
-t1, --tplDaoIndexPath template file path for dao index file
-t2, --tplDaoInternalPath template file path for dao internal file
-t3, --tplDaoDoPath template file path for dao do file
-t4, --tplDaoEntityPath template file path for dao entity file
-s, --stdTime use time.Time from stdlib instead of gtime.Time for generated time/date fields of tables
-w, --withTime add created time for auto produced go files
-n, --gJsonSupport use gJsonSupport to use *gjson.Json instead of string for generated json fields of
tables
-v, --overwriteDao overwrite all dao files both inside/outside internal folder
-c, --descriptionTag add comment to description tag for each field
-k, --noJsonTag no json tag will be added for each field
-m, --noModelComment no model comment will be added for each field
-a, --clear delete all generated go files that do not exist in database
-gt, --genTable generate table files
-y, --typeMapping custom local type mapping for generated struct attributes relevant to fields of table
-fm, --fieldMapping custom local type mapping for generated struct attributes relevant to specific fields of
table
-/--genItems
-h, --help more information about this command
EXAMPLE
gf gen dao
gf gen dao -l "mysql:root:12345678@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/test"
gf gen dao -p ./model -g user-center -t user,user_detail,user_login
gf gen dao -r user_
CONFIGURATION SUPPORT
Options are also supported by configuration file.
It's suggested using configuration file instead of command line arguments making producing.
The configuration node name is "gfcli.gen.dao", which also supports multiple databases, for example(config.yaml):
gfcli:
gen:
dao:
- link: "mysql:root:12345678@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/test"
tables: "order,products"
jsonCase: "CamelLower"
- link: "mysql:root:12345678@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/primary"
path: "./my-app"
prefix: "primary_"
tables: "user, userDetail"
typeMapping:
decimal:
type: decimal.Decimal
import: github.com/shopspring/decimal
numeric:
type: string
fieldMapping:
table_name.field_name:
type: decimal.Decimal
import: github.com/shopspring/decimal
If using the framework-recommended project engineering scaffold and the system has the make tool installed, the shortcut command make dao can also be used.
Configuration Example
File configuration example:
gfcli:
gen:
dao:
- link: "mysql:root:12345678@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/test"
tables: "order,products"
jsonCase: "CamelLower"
- link: "mysql:root:12345678@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/primary"
path: "./my-app"
prefix: "primary_"
tables: "user, userDetail"
# sqlite requires manual compilation of gf with sqlite driver, modify the import path file (gf\cmd\gf\internal\cmd\cmd_gen_dao.go) to uncomment for sqlite driver, gcc is required for sqlite driver
- link: "sqlite:./file.db"
Parameter Description
| Name | Default Value | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
gfcli.gen.dao | dao code generation configuration items, can have multiple configuration items to form an array, supporting multiple database generation. Different databases can set different generation rules, for example, they can be generated to different locations or files. | - | |
link | Required Parameter. It consists of two parts, the first part represents your connected database type mysql, postgresql, etc., while the second part is the dsn information for the connection. For specific details, please refer to the section ORM - Configuration. | - | |
path | internal | The storage directory address for generated dao and model files. | ./app |
group | default | Database group name in the database configuration. Only one name can be configured. The group name in the database configuration file is often not modified once determined. | defaultorderuser |
prefix | Prefixes for the generated database objects and files to distinguish between different databases or the same table names in different databases, to prevent data table name overwriting. | order_user_ | |
removePrefix | Removes specified prefix names from data tables. Multiple prefixes are separated by commas. | gf_ | |
removeFieldPrefix | Removes specified prefix names from field names. Multiple prefixes are separated by commas. | f_ | |
tables | Specifies which tables in the current database need code generation. If empty, all tables in the database will be generated. | user, user_detail | |
tablesEx | Tables Excluding, specifies which tables in the current database are excluded from code generation. | product, order | |
jsonCase | CamelLower | Specifies the naming rules for json tags in generated data entity objects in model, the parameter is case-insensitive. Optional parameters: Camel, CamelLower, Snake, SnakeScreaming, SnakeFirstUpper, Kebab, KebabScreaming. For a detailed introduction, please refer to the command line help example. | Snake |
stdTime | false | When a data table field type is a time type, the generated property type uses the standard library time.Time instead of the framework's *gtime.Time type. | true |
withTime | false | Adds generation time comments to each automatically generated code file | |
gJsonSupport | false | When a data table field type is JSON, the generated property type uses *gjson.Json type. | true |
overwriteDao | false | Whether to regenerate and overwrite files outside the dao/internal directory for each dao code generation. Note that files outside the dao/internal directory may have been custom extended by the developer, and overwriting may introduce risk. | true |
importPrefix | Automatically detected via go.mod | Used to specify the import path prefix for generated Go files. Especially necessary when the gen dao command is not used at the project's root directory or when intending to generate code files to a custom directory. | github.com/gogf/gf |
descriptionTag | false | Specifies whether to add a description tag with the schema for each data model struct field, where the content is the corresponding data table field comment. | true |
noJsonTag | false | The generated data model does not include json tags for fields | |
noModelComment | false | Specifies whether to disable automatic generation of comments for model struct fields, where the content is derived from the data table field comments. | true |
clear | false | Automatically deletes local dao/do/entity code files that do not correspond to any data tables in the database. Use this parameter with caution! | |
daoPath | dao | Directory for storing generated DAO files | |
doPath | model/do | Directory for storing generated DO files | |
entityPath | model/entity | Directory for storing generated Entity files | |
tablePath | table | Directory for storing generated Table files | |
tplDaoIndexPath | Custom DAO Index code generation template file path, please refer to the source code for use | ||
tplDaoInternalPath | Custom DAO Internal code generation template file path, please refer to the source code for use | ||
tplDaoDoPath | Custom DO code generation template file path, please refer to the source code for use | ||
tplDaoEntityPath | Custom Entity code generation template file path, please refer to the source code for use | ||
tplDaoTablePath | Custom Table code generation template file path, please refer to the source code for use | ||
typeMapping | Supported from version v2.5. Used to customize the mapping of data table fields types to corresponding types in generated Go files. | ||
fieldMapping | Supported from version v2.8. Used to customize the mapping of specific data table fields to corresponding field types in generated Go files. | ||
shardingPattern | Supported from version v2.9. Used to customize data table sharding rules. | ||
genTable | false | Supported from version v2.9.5. Used to control whether to generate database table field definition files. Each table will generate a corresponding Go file containing detailed definitions of all fields in that table, such as field name, type, index, whether nullable, etc. These generated files are mainly used for gdb to internally understand table structure. Each table has a SetXxxTableFields function that can register table field definitions to the database instance. | true |
Parameter: typeMapping
The typeMapping parameter supports configuring the database field types corresponding to Go data types, and the default value is:
decimal:
type: float64
money:
type: float64
numeric:
type: float64
smallmoney:
type: float64
This configuration supports importing third-party packages via the import configuration item, for example:
decimal:
type: decimal.Decimal
import: github.com/shopspring/decimal
Parameter: fieldMapping
The fieldMapping parameter provides fine-grained field type mapping configuration, supporting the configuration of specific database fields' generated Go data types. Apart from a different configuration name, the configuration content is the same as typeMapping. Example configuration:
paid_orders.amount:
type: decimal.Decimal
import: github.com/shopspring/decimal
In the example, paid_orders is the table name, amount is the field name, type represents the data type name in the generated Go code, and import represents third-party packages that need to be imported in the generated code.
Parameter: shardingPattern
The shardingPattern parameter is used to configure sharding rules. This parameter was added in version v2.9 to identify and handle sharding tables. Sharding tables are multiple tables with the same structure that are split according to certain rules, such as time-based sharding tables like orders_202301, orders_202302, or user ID-based sharding tables like users_0001, users_0002.
Parameter Description
- Type: String array
- Format: Use
?as a wildcard to match the sharding part in table names - Purpose: Identify multiple tables matching the same pattern as a single logical table and generate sharding-enabled
DAOcode
How It Works
When using the shardingPattern parameter, the gen dao command will:
- Match table names in the database according to the provided pattern
- Identify multiple tables matching the same pattern as a single logical table
- Remove the sharding identifier part from the table name
- Generate sharding-enabled
DAOcode for that logical table
Parameter Example
Suppose the database has the following tables:
users_0001
users_0002
users_0003
products
Using the following shardingPattern configuration:
gendao:
- link: "mysql:root:12345678@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/test"
shardingPattern:
- "users_?"
The generated result will include:
- A
DAOfile namedusers.go, instead of generating separateDAOfiles for each sharding table - The
DAOfile will contain sharding configuration code to automatically handle operations on different sharding tables - The products table will generate a normal
products.goDAOfile
Generated DAO file example:
// ...
type usersDao struct {
*internal.UsersDao
}
var (
// Users is a globally accessible object for table users_0001 operations.
Users = usersDao{internal.NewUsersDao(userShardingHandler)}
)
// userShardingHandler is the handler for sharding operations.
// You can fill this sharding handler with your custom implementation.
func userShardingHandler(m *gdb.Model) *gdb.Model {
m = m.Sharding(gdb.ShardingConfig{
Table: gdb.ShardingTableConfig{
Enable: true,
Prefix: "",
// Replace Rule field with your custom sharding rule.
// Or you can use "&gdb.DefaultShardingRule{}" for default sharding rule.
Rule: nil,
},
Schema: gdb.ShardingSchemaConfig{},
})
return m
}
// ...
You need to set the sharding rules in the Sharding function within the userShardingHandler function in the DAO file, and you can also set database sharding rules. If you generate sharding DAO files but do not manually set the sharding rules, calling the DAO object directly will result in an error.
Multiple Sharding Patterns
Configuration example for specifying multiple sharding patterns simultaneously:
gendao:
- link: "mysql:root:12345678@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/test"
shardingPattern:
- "users_?"
- "orders_?"
This will process sharding tables with both users_ and orders_ prefixes, generating users.go and orders.go DAO files.
Notes
- Sharding tables must have the same table structure.
- The sharding identifier can be numbers, dates, or other formats, as long as it can be matched with the
?wildcard. - The generated
DAOcode will automatically include all matching sharding tables. If new sharding tables are added later, you need to regenerate theDAOcode. - You need to add a
Shardingmethod for each sharding table in the generatedDAOfile to specify the sharding rules. Please refer to the section: ORM Sharding - Table Sharding Feature.
Parameter: genTable
The genTable parameter is used to control whether to generate database table field definition files. This parameter was added in version v2.9.5. Each table will generate a corresponding Go file containing detailed definitions of all fields in that table, such as field name, type, index, whether nullable, etc. These generated files are mainly used for gdb to internally understand table structure, and include a SetXxxTableFields function.
Registering table field information to the database instance allows gdb to build SQL without relying on the actual database connection, making it convenient for users to use ToSQL and CatchSQL to directly obtain the final SQL.
Generated Table file example:
// =================================================================================
// This file is auto-generated by the GoFrame CLI tool. You may modify it as needed.
// =================================================================================
package table
import (
"context"
"github.com/gogf/gf/v2/database/gdb"
)
// User defines the fields of table "user" with their properties.
// This map is used internally by GoFrame ORM to understand table structure.
var User = map[string]*gdb.TableField{
"id": {
Index: 0,
Name: "id",
Type: "bigint",
Null: false,
Key: "PRI",
Default: nil,
Extra: "auto_increment",
Comment: "",
},
"tenant_id": {
Index: 1,
Name: "tenant_id",
Type: "varchar(64)",
Null: false,
Key: "MUL",
Default: nil,
Extra: "",
Comment: "",
},
"username": {
Index: 2,
Name: "username",
Type: "varchar(100)",
Null: false,
Key: "",
Default: nil,
Extra: "",
Comment: "",
},
"email": {
Index: 3,
Name: "email",
Type: "varchar(150)",
Null: true,
Key: "",
Default: nil,
Extra: "",
Comment: "",
},
"created_at": {
Index: 4,
Name: "created_at",
Type: "datetime(3)",
Null: false,
Key: "",
Default: "CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(3)",
Extra: "DEFAULT_GENERATED",
Comment: "",
},
"updated_at": {
Index: 5,
Name: "updated_at",
Type: "datetime(3)",
Null: false,
Key: "",
Default: "CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(3)",
Extra: "DEFAULT_GENERATED on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(3)",
Comment: "",
},
"deleted_at": {
Index: 6,
Name: "deleted_at",
Type: "datetime(3)",
Null: true,
Key: "MUL",
Default: nil,
Extra: "",
Comment: "",
},
}
// SetUserTableFields registers the table fields definition to the database instance.
// db: database instance that implements gdb.DB interface.
// schema: optional schema/namespace name, especially for databases that support schemas.
func SetUserTableFields(ctx context.Context, db gdb.DB, schema ...string) error {
return db.GetCore().SetTableFields(ctx, "user", User, schema...)
}
Usage Example
Repository address: https://github.com/gogf/focus-single
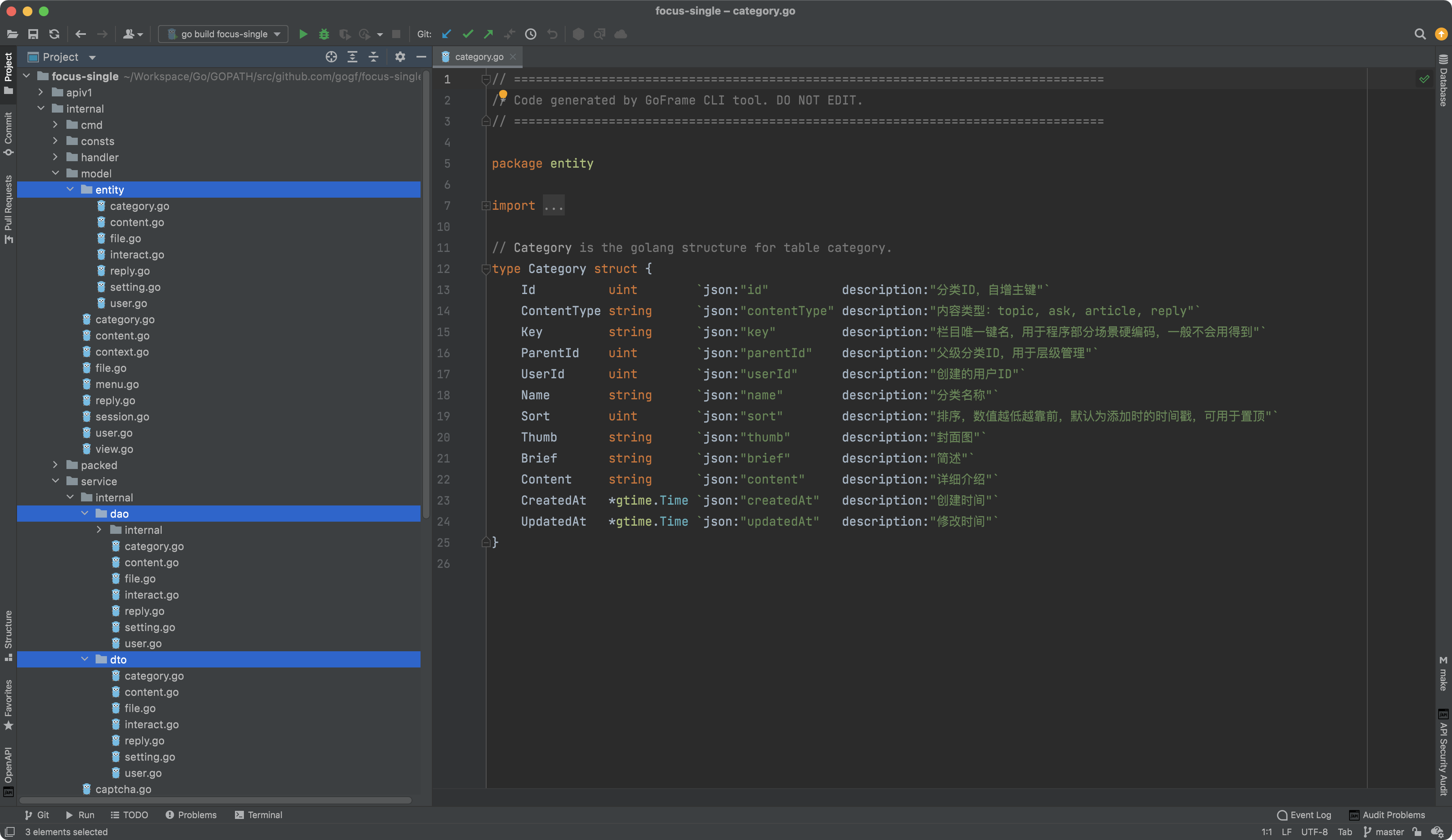
- Files in the following
3directories are generated by thedaocommand:
| Path | Description | Detailed Introduction |
|---|---|---|
/internal/dao | Data Access Object | Accesses the underlying data source through the object-oriented way, based on the ORM component. Often used in combination with entity and do. Files in this directory can be extended and modified by developers. |
/internal/model/do | Data Transformation Model | The data transformation model is used for converting business models to data models, maintained by tools, and should not be modified by users. The tool will overwrite this directory each time code files are generated. For an introduction to do files, please refer to:- Data and Business Models - Pain Points and Improvements In Business Project - Utilizing Pointer Properties and Do Objects for Flexible Modification Interfaces |
/internal/model/entity | Data Model | The data model is maintained by tools and should not be modified by users. The tool will overwrite this directory each time code files are generated. |
- Models in the
modeldirectory are divided into two categories: Data Models and Business Models.
Data Models: Automatically generated by the CLI tool in the model/entity directory. The database tables will all be generated in this directory, and the files in this directory correspond to data models. Data models are data structures that correspond one-to-one with database tables; developers usually do not need to modify them and should not, as data models are automatically updated by the CLI tool when there are changes to the database table structures. Data models are generated and maintained uniformly by the CLI tool.
Business Models: Business models are data structures related to the business, defined as needed, such as service input and output data structure definitions and some internal data structure definitions. Business models are defined and maintained by developers according to business needs, defined in the model directory.
- Files in the
daofolder are named after database table names, with one file and its correspondingDAOobject for each database table. Operations on database tables are implemented throughDAOobjects and related methods. Thedaooperation adopts a standardized design, requiring thectxparameter to be passed, and the generated code must be operated by creating objects through theCtxorTransactionmethod to chain operation on database tables.
Notes
Databases Requiring Manual Compilation
The gen dao command involves data access-related code generation and supports several commonly used database types by default. If Oracle database support is needed, developers must modify the source code files and manually compile and install the CLI tool locally, as the driver for these databases require CGO support and cannot be precompiled for general use.
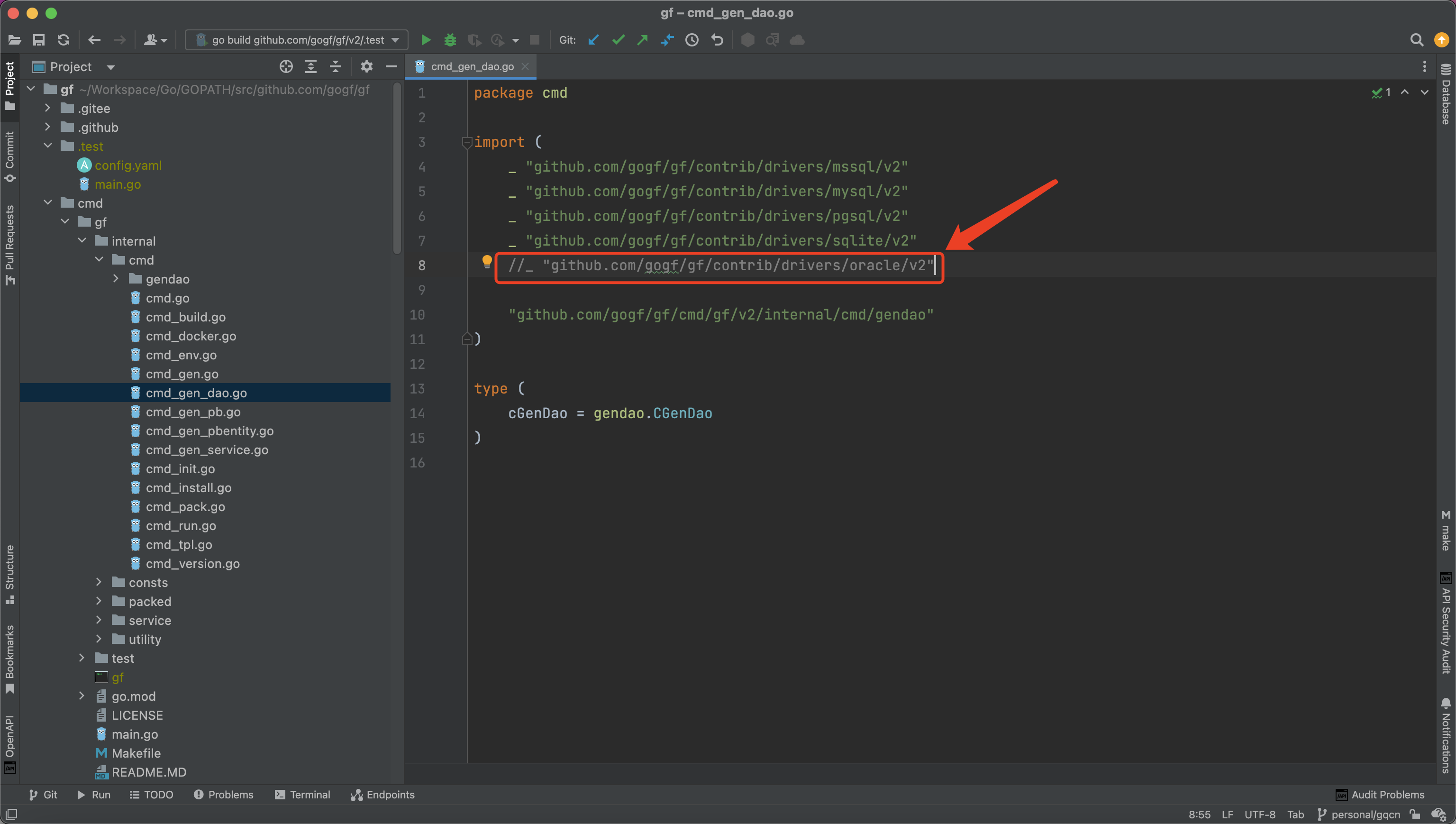
About bool Type Corresponding to Database Table Fields
Since most database types do not have bool type table field types,
we recommend using bit(1) to represent a field’s bool type instead of tinyint(1) or int(1). Because the tinyint(1)/int(1) field type represents a range of -127~127, it is usually used as a status field type. While the bit(1) type range is 0/1, which can accurately represent the bool type's two values false/true.
For example, table fields:

Generated properties: